"Schema Mark-up" is a kind of structured data that comprises a few lines of HTML code that can be added to web pages. Whilst this is invisible to your website's visitors, it should only be applied to content that is visible to them, with the purpose of providing search engines with additional information about the content of your web pages. The guidelines for using such code have been collaboratively created by Google, Microsoft, and Yahoo! together, at Schema.org, meaning that just one integration will benefit your website in all the major search engines. Adding schema mark-up to your website's pages can result in the following benefits to your Search Engine Optimization (SEO) efforts:
- It may improve how search engines understand your website's content, possibly resulting in higher rankings in search results
- It may improve the text shown alongside your web pages in search results, possibly resulting in more users clicking on the result associated with your website
How Schema Mark-Up May Improve Your Search Engine Rankings
Schema mark-up that accurately reflects the content of your web pages helps search engines to interpret both the content of your pages and it's context. "In general, the more markup there is, the easier it is for search engines to be able to interpret what really matters on a page," explains Matt Cutts, head of the Webspam team at Google.
Since the tools that search engines use to index the internet ("spiders") are in fact machines, they can't always understand the relevance of a particular web page in relation to a search term. An example of this provided by Schema.org imagines a scenario where your web page is titled "Avatar". However, this does not give any information about whether this refers to the movie, a profile picture, or something else entirely. Schema mark-up allows you to add special tags to your web pages to help search engines categorize and add context to your website's content.
Helping search engines better understand your website's content and it's context may improve your search engine rankings for particular search terms and, with Google's increasing shift towards "semantic" search, schema mark-up is going to become ever more important.
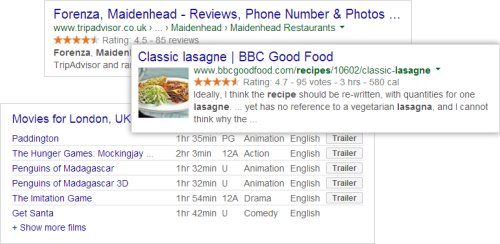
How Schema Mark-Up May Improve Your Website's "Snippets"
Alongside each search result returned by all the major search engines is a "Snippet" - a few lines of text designed to give a sense of what the page in question is about and why it's relevant to the search. If schema mark-up is present on a web page, Google may use this to create a more enhanced Snippet - called a "Rich Snippet" to display in search results for that web page (unless it has taken a "manual action" to ignore the schema mark-up of a spam website because it does not accurately reflect the site's content). Google supports schema mark-up to create Rich Snippets for an ever-growing range of content types, currently including articles, books, courses, reviews, ratings, events, FAQs, job postings, local business listings, logos, movies, products, recipes and videos. You can control which specific web pages (and even what parts of specific pages) that Google can use to create rich snippets using any of the supported "robots tag" attributes for snippets.
A Rich Snippet being returned for your web pages in a user's search results can result in two possible outcomes:
- The user will see that your web page contains exactly the information they need and will therefore choose that search result and visit your website. For example, if the Snippet for your web page is "A review of the best courier services in London" and that's both exactly what your page contains and what the person performing the search is looking for, you will benefit from more clicks on your search result than if the Snippet was less informative.
- The user will get the information they need from the Snippet, with no need to visit your web page. While this might not be an instinctive goal of search engine optimization, there are instances where it might be useful. For example, a cinema company can display up-to-date film times within the Snippets of it's web pages. In this instance, the fact that a person searching for "film times" will not have to visit the company's website will probably not harm the company's ultimate goal (of selling cinema tickets).
Should You Add Schema Mark-Up To Your Website?
Whether or not the addition of schema mark-up would benefit your website depends on what type of data it consists of:
- Websites that consist of little more than a few pages of information (e.g. a small business website) are unlikely to benefit from any change in search engine ranking in the short-term.
- Websites that contain any kind of content that can be categorized (such as image galleries, reviews, blog entries, articles, videos or discussions) may experience a slight improvement in search engine rankings. Since even a small difference in position can yield significant additional sales, we recommend that such websites consider using schema mark-up.
- Websites that include any kind of data relating to events or "things" (such as albums, books, movies, recipes, locations etc) would potentially benefit the most, through improved search engine rankings and an increased number of clicks from search results due to the use of Rich Snippets. We strongly recommend that such websites consider using schema mark-up.
It is clear that search engines will place more and more emphasis on schema mark-up, with Google stating that "over time you can expect that more data will be used in more ways". Therefore, regardless of your website's content, but particularly if your website includes data relating to events or "things", adding schema mark-up to your website is probably something that will be required in the future if you want to make sure that your competition is not gaining an advantage over you.
Last updated: 3rd December, 2019


